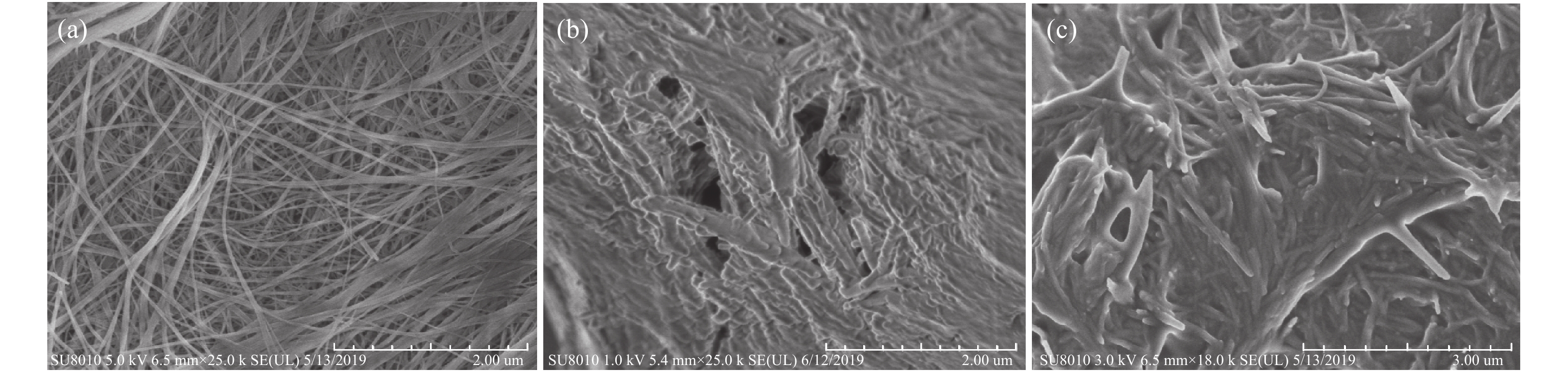
Preparation and properties of hydroxyapatite aerogel composite phase change materials
-
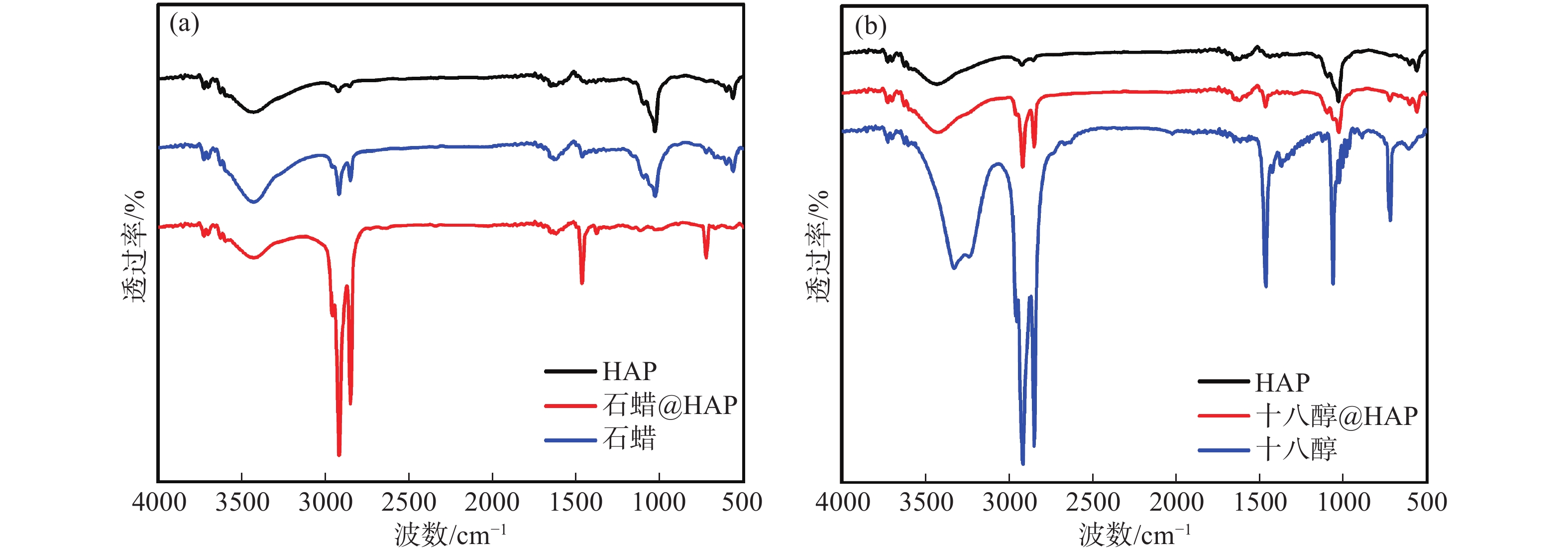
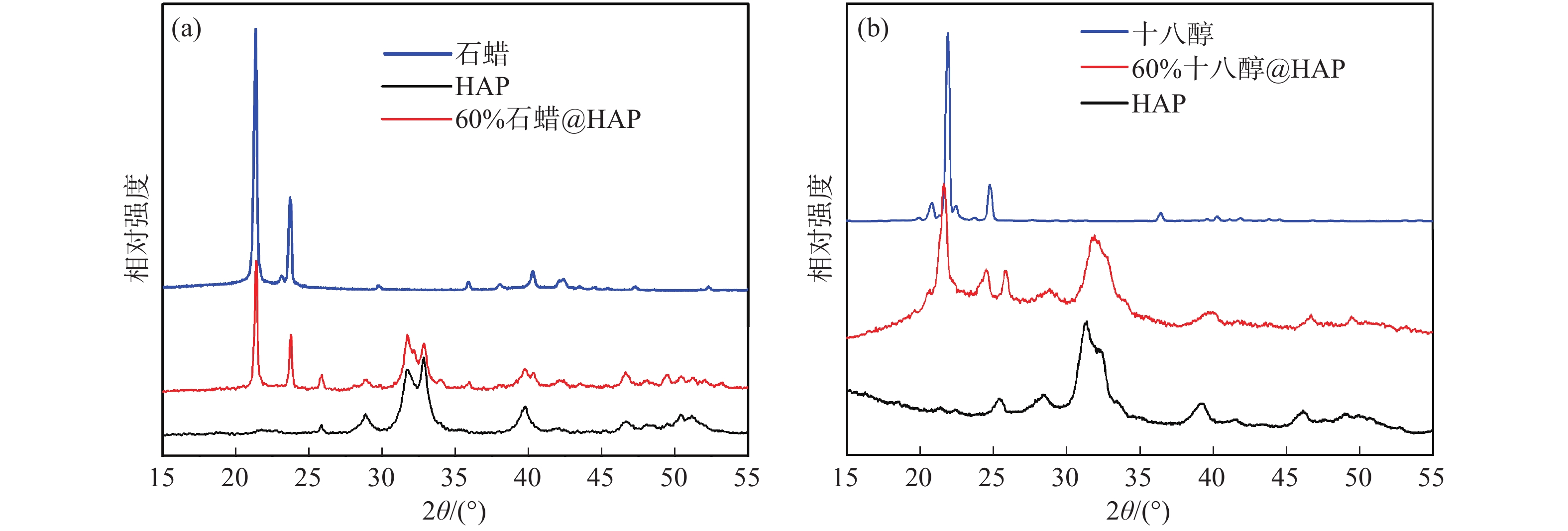
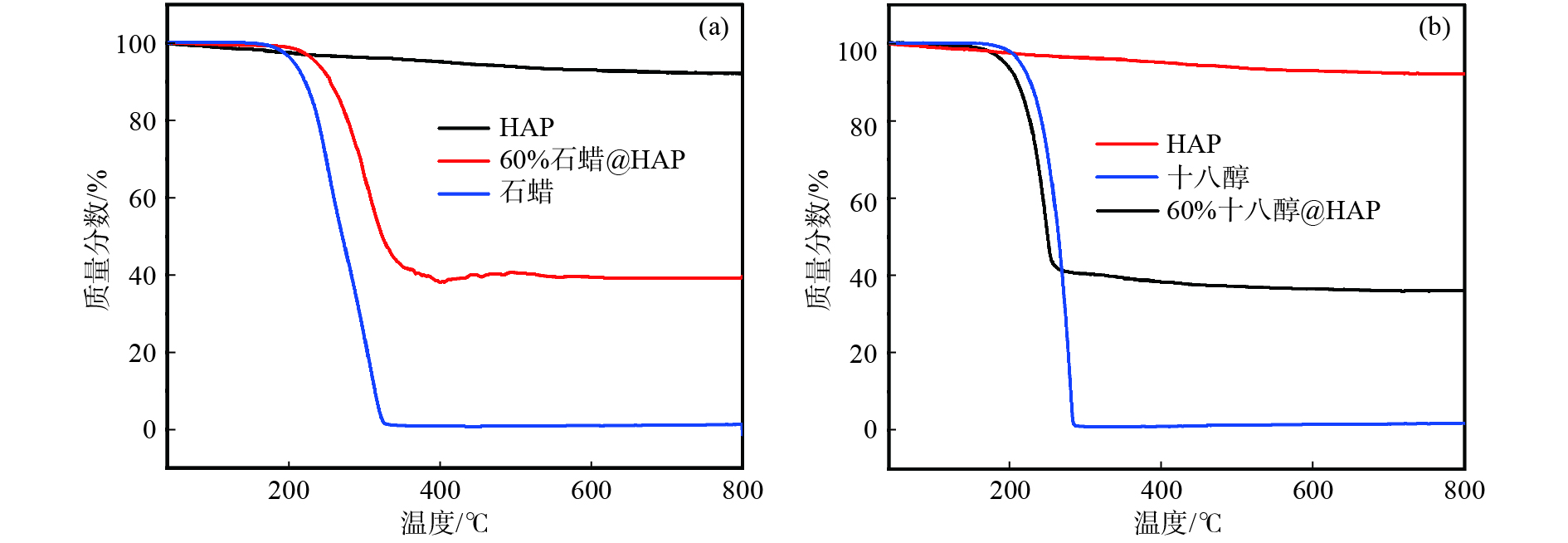
摘要: 以相變材料為核心的潛熱儲存技術,對加快新能源開發和提高能源利用率起著關鍵性作用。以油酸鈣為前驅體,通過水熱法合成了具有自支撐網絡結構的羥基磷灰石(HAP)氣凝膠,并采用浸漬法制備出自支撐羥基磷灰石復合相變材料。通過掃描電鏡、傅里葉紅外光譜、X射線衍射、熱重法、差示掃描量熱法等手段對所制備復合相變材料的形貌、穩定性、熱性能等進行了表征及測試。實驗結果表明,負載石蠟或十八醇的羥基磷灰石氣凝膠復合相變材料均具有良好的熱性能,質量分數60%石蠟@HAP氣凝膠復合相變材料的熔融焓和凝固焓測量值分別為85.10和85.30 J·g?1,結晶度為81.50%;質量分數60%十八醇@HAP氣凝膠復合相變材料的熔融焓和凝固焓測量值為113.78和112.25 J·g?1,結晶度為86.20%,且具有很好的熱穩定性和化學穩定性。此外,羥基磷灰石氣凝膠載體材料阻燃性好,無腐蝕且安全環保,有效拓展了相變材料在智能保溫紡織物和建筑材料等領域的實際應用。Abstract: To address energy shortage and environmental pollution, scientists are working to develop methods for the production, conversion, and storage of new energy sources. The development of thermal energy storage (TES) is considered to be one of the most effective energy conservation and environmental protection strategies for utilizing various renewable energy sources. Energy storage technology can solve the contradiction between energy supply and demand in time and space and also improve energy efficiency. Currently, TES includes mainly sensible heat storage, latent heat storage, and thermochemical energy storage. The latent heat TES based on phase change materials (PCMs) is an efficient technology that is being actively pursued owing to high storage density in a small temperature region, which is essential for accelerating new energy development and improving energy efficiency. In this paper, hydroxyapatite aerogels with self-supporting network structure were prepared via a hydrothermal method using calcium oleate as a precursor. Self-supporting hydroxyapatite-based composite phase change materials were synthesized using the impregnation method. The morphology and thermal properties of the prepared composite phase change materials were characterized and tested by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry, and differential scanning calorimetry. The experimental results show that the composite phase change materials of hydroxyapatite aerogels loaded with octadecanol or paraffin have good thermal properties. The measured values of melting enthalpy and solidified enthalpy of the 60% paraffin@HAP composite phase change materials are 85.10 and 85.30 J·g?1, respectively, and its crystallinity is 81.50%. The measured values of melting enthalpy and solidified enthalpy of the 60% octadecanol@HAP composite phase change material are 113.78 and 112.25 J·g?1, respectively, and its crystallinity is 86.20%. In addition, the composite has good thermal and chemical stability. Furthermore, the hydroxyapatite substrate has the advantages of good flame retardancy, corrosion-free characteristics, safety, and environmental protection, which effectively expands the practical application of phase change materials in the field of intelligent thermal insulation textiles and building materials.
-
Key words:
- phase change materials /
- hydroxyapatite /
- paraffin /
- octadecanol /
- latent heat /
- fire resistance
-
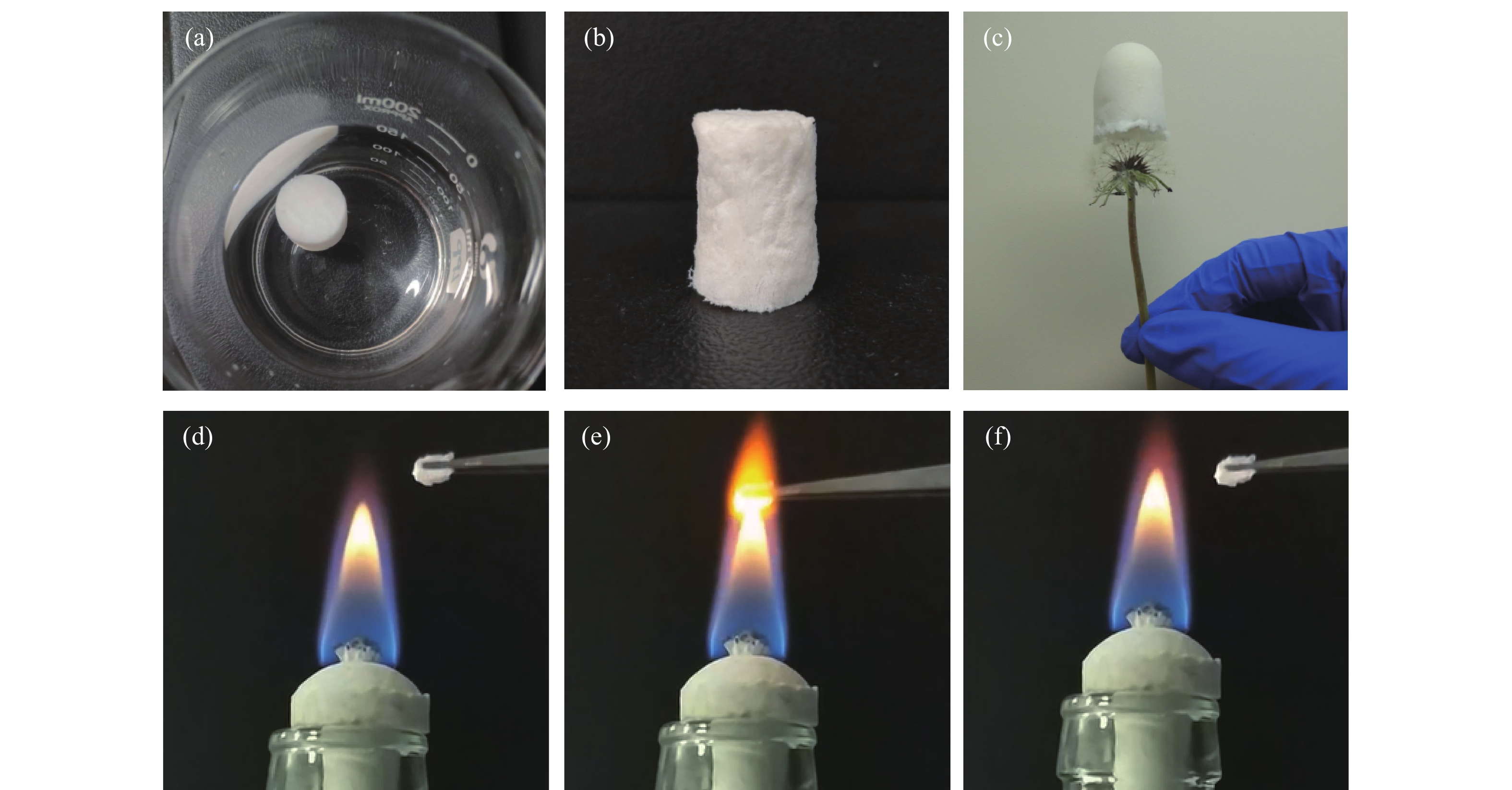
圖 3 HAP氣凝膠的數碼照片.(a) HAP氣凝膠冷凍干燥前;(b) HAP氣凝膠冷凍干燥后;(c) 蒲公英頂部的HAP氣凝膠;(d)HAP氣凝膠燃燒前;(e) HAP氣凝膠燃燒中;(f) HAP氣凝膠燃燒后
Figure 3. Digital images of HAP aerogels: (a) HAP aerogels before freeze-dried; (b) HAP aerogels after freeze-dried; (c) HAP aerogels on top of the dandelion; (d) HAP aerogels before combustion; (e) HAP aerogels in combustion; (f) HAP aerogels after combustion
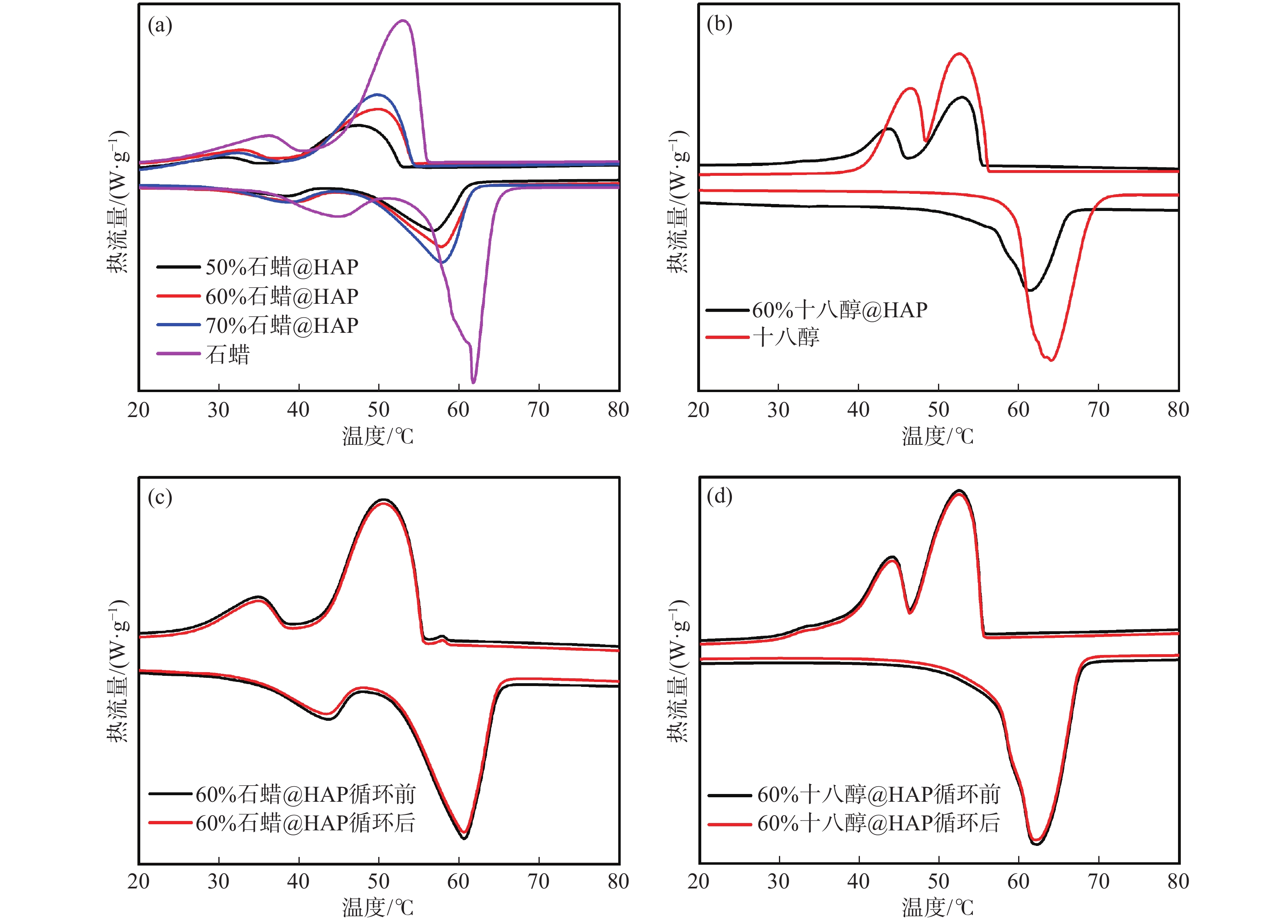
圖 7 復合相變材料差示掃描量熱分析曲線.(a) 石蠟及復合相變材料;(b) 十八醇及復合相變材料;(c) 石蠟復合相變材料循環20次前后;(d) 十八醇復合相變材料循環20次前后
Figure 7. DSC curves of composite PCMs: (a) paraffin and composite PCMs; (b) octadecanol and composite PCMs; (c) paraffin composite before and after 20 times cycling; (d) octadecanol composite before and after 20 times thermal cycling
表 1 HAP氣凝膠相變復合材料的熱性能
Table 1. Thermal properties of HAP aerogel composite PCMs
相變材料 負載量/% Tm/℃ Tf/℃ $\Delta {H_{\rm{m}}}$/(J·g?1) $\Delta {H_{\rm{f}}}$/(J·g?1) 石蠟 100 61.73 55.97 176.97 174.45 石蠟@HAP 60 57.68 47.81 85.10 85.30 十八醇 100 63.98 52.59 221.01 218.75 十八醇@HAP 60 61.40 53.03 113.78 112.25 中文字幕在线观看表 2 60%石蠟@HAP復合相變材料和文獻中石蠟復合相變材料的熱性能對比
Table 2. Thermal performance comparison of 60% paraffin@HAP composite PCMs and paraffin composite PCMs in literature
-
參考文獻
[1] Aftab W, Huang X Y, Wu W H, et al. Nanoconfined phase change materials for thermal energy applications. Energy Environ Sci, 2018, 11(6): 1392 doi: 10.1039/C7EE03587J [2] Gao H Y, Wang J J, Chen X, et al. Nanoconfinement effects on thermal properties of nanoporous shape-stabilized composite PCMs: A review. Nano Energy, 2018, 53: 769 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.09.007 [3] Umair M M, Zhang Y A, Iqbal K, et al. Novel strategies and supporting materials applied to shape-stabilize organic phase change materials for thermal energy storage–a review. Appl Energy, 2019, 235: 846 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.11.017 [4] Akhiani A R, Mehrali M, Latibari S T, et al. One-step preparation of form-stable phase change material through self-assembly of fatty acid and graphene. J Phys Chem C, 2015, 119(40): 22787 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06089 [5] Huang X Y, Liu Z P, Xia W, et al. Alkylated phase change composites for thermal energy storage based on surface-modified silica aerogels. J Mater Chem A, 2015, 3(5): 1935 doi: 10.1039/C4TA06735E [6] Wang J J, Yang M, Lu Y F, et al. Surface functionalization engineering driven crystallization behavior of polyethylene glycol confined in mesoporous silica for shape-stabilized phase change materials. Nano Energy, 2016, 19: 78 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.11.001 [7] Chen X, Gao H, Yang M, et al. Smart integration of carbon quantum dots in metal-organic frameworks for fluorescence-functionalized phase change materials. Energy Storage Mater, 2019, 18: 349 doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2018.08.015 [8] Scaffaro R, Maio A, Lopresti F, et al. Synthesis and self-assembly of a PEGylated-graphene aerogel. Compos Sci Technol, 2016, 128: 193 doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.03.030 [9] Fang Y T, Zou T, Liang X H, et al. Self-assembly synthesis and properties of microencapsulated n-tetradecane phase change materials with a calcium carbonate shell for cold energy storage. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng, 2017, 5(4): 3074 doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02758 [10] Wang W, Wang C Y, Wang T, et al. Enhancing the thermal conductivity of n-eicosane/silica phase change materials by reduced graphene oxide. Mater Chem Phys, 2014, 147(3): 701 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.009 [11] Xia Y P, Cui W W, Zhang H Z, et al. Synthesis of three-dimensional graphene aerogel encapsulated n-octadecane for enhancing phase-change behavior and thermal conductivity. J Mater Chem A, 2017, 5(29): 15191 doi: 10.1039/C7TA03432F [12] Qian T T, Li J H, Ma H W, et al. The preparation of a green shape-stabilized composite phase change material of polyethylene glycol/SiO2 with enhanced thermal performance based on oil shale ash via temperature-assisted sol-gel method. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2015, 132: 29 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2014.08.017 [13] Yang J, Qi G Q, Liu Y, et al. Hybrid graphene aerogels/phase change material composites: thermal conductivity, shape-stabilization and light-to-thermal energy storage. Carbon, 2016, 100: 693 doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.01.063 [14] Chen F, Zhu Y J. Large-scale automated production of highly ordered ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and construction of various fire-resistant flexible ordered architectures. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 11483 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07239 [15] Lyu J, Liu Z W, Wu X H, et al. Nanofibrous Kevlar aerogel films and their phase-change composites for highly efficient infrared stealth. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 2236 [16] Zhang Y G, Zhu Y J, Xiong Z C, et al. Bioinspired ultralight inorganic aerogel for highly efficient air filtration and oil-water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10(15): 13019 doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b02081 [17] Xiong Z C, Yang R L, Zhu Y J, et al. Flexible hydroxyapatite ultralong nanowire-based paper for highly efficient and multifunctional air filtration. J Mater Chem A, 2017, 5(33): 17482 doi: 10.1039/C7TA03870D [18] Zhong L M, Yang M, Luan Y, et al. Preparation and properties of paraffin/SiO2 composite phase change materials. Chin J Eng, 2015, 37(7): 936鐘麗敏, 楊穆, 欒奕, 等. 石蠟/二氧化硅復合相變材料的制備及其性能. 工程科學學報, 2015, 37(7):936 [19] Tang J, Yang M, Yu F, et al. 1-Octadecanol@ hierarchical porous polymer composite as a novel shape-stability phase change material for latent heat thermal energy storage. Appl Energy, 2017, 187: 514 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.11.043 [20] Yu H P, Zhu Y J, Lu B Q. Highly efficient and environmentally friendly microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. Ceram Int, 2018, 44(11): 12352 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.022 [21] Han L, Jia X L, Li Z M, et al. Effective encapsulation of paraffin wax in carbon nanotube agglomerates for a new shape-stabilized phase change material with enhanced thermal-storage capacity and stability. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2018, 57(39): 13026 doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b02159 [22] Ayd?n A A. High-chain fatty acid esters of 1-octadecanol as novel organic phase change materials and mathematical correlations for estimating the thermal properties of higher fatty acid esters homologous series. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2013, 113: 44 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.01.024 [23] Chen X, Gao H Y, Xing L W, et al. Nanoconfinement effects of N-doped hierarchical carbon on thermal behaviors of organic phase change materials. Energy Storage Mater, 2019, 18: 280 doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2018.08.024 [24] Qian T T, Li J H, Min X, et al. Integration of pore confinement and hydrogen-bond influence on the crystallization behavior of C18 PCMs in mesoporous silica for form-stable phase change materials. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng, 2018, 6(1): 897 doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03267 [25] Chen X, Gao H Y, Yang M, et al. Highly graphitized 3D network carbon for shape-stabilized composite PCMs with superior thermal energy harvesting. Nano Energy, 2018, 49: 86 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.03.075 [26] Li S H, Shao J Y, Zhang P Z, et al. Preparation of micro-encapsulated phase change materials and its composite materials development. Appl Chem Ind, 2015, 44(5): 937李淑慧, 邵競堯, 張鵬中, 等. 相變儲能微膠囊的制備及其復合材料的研究進展. 應用化工, 2015, 44(5):937 [27] Zhao S X, Yan H, Li Y T, et al. Structure and thermal performances of paraffin/diatomite form-stable phase change materials. Chin J Mater Res, 2017, 31(7): 502 doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2016.640趙思勰, 晏華, 李云濤, 等. 石蠟/硅藻土定型相變材料的結構和熱性能. 材料研究學報, 2017, 31(7):502 doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2016.640 [28] Tong X M, Hao Q Q, Liu Z W, et al. Preparation and property of paraffin phase change microcapsule modified by graphene oxide. New Chem Mater, 2018, 46(5): 107童曉梅, 郝芹芹, 劉智偉, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性石蠟相變微膠囊的制備及性能研究. 化工新型材料, 2018, 46(5):107 [29] Qiu X Z. Synthesis and Charcaterization of Paraffin/TiO2-P (MMA-co-BA) Phase Change Material Microcapsules for Thermal Energy Storage[Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018邱曉忠. 石蠟/TiO2-P (MMA-co-BA) 相變材料儲能微膠囊的制備和性能研究[學位論文]. 廣州: 華南理工大學, 2018 -




 下載:
下載: