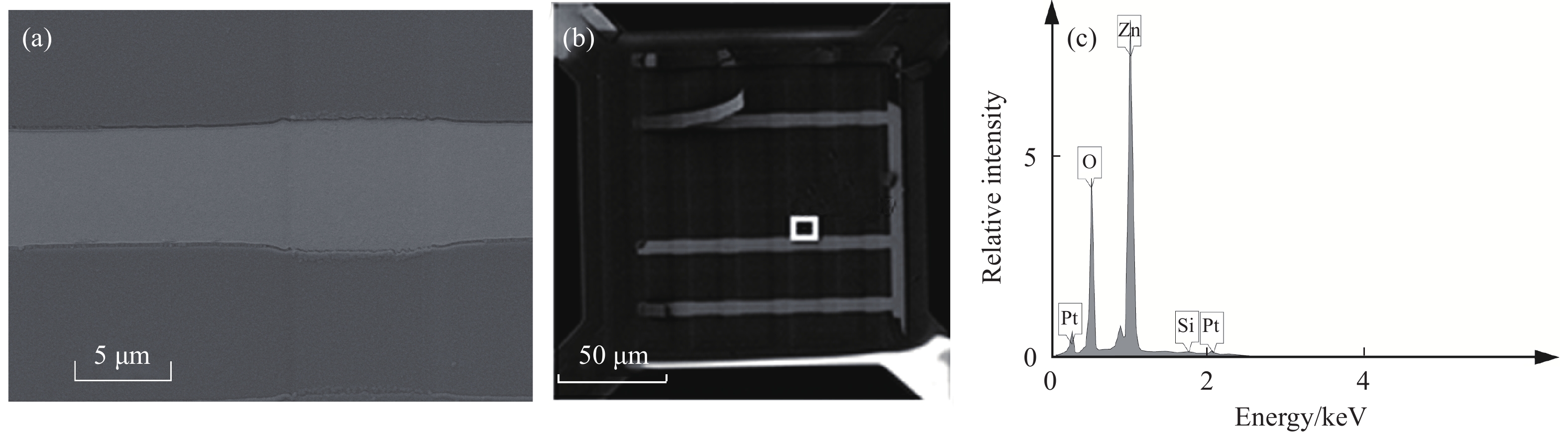
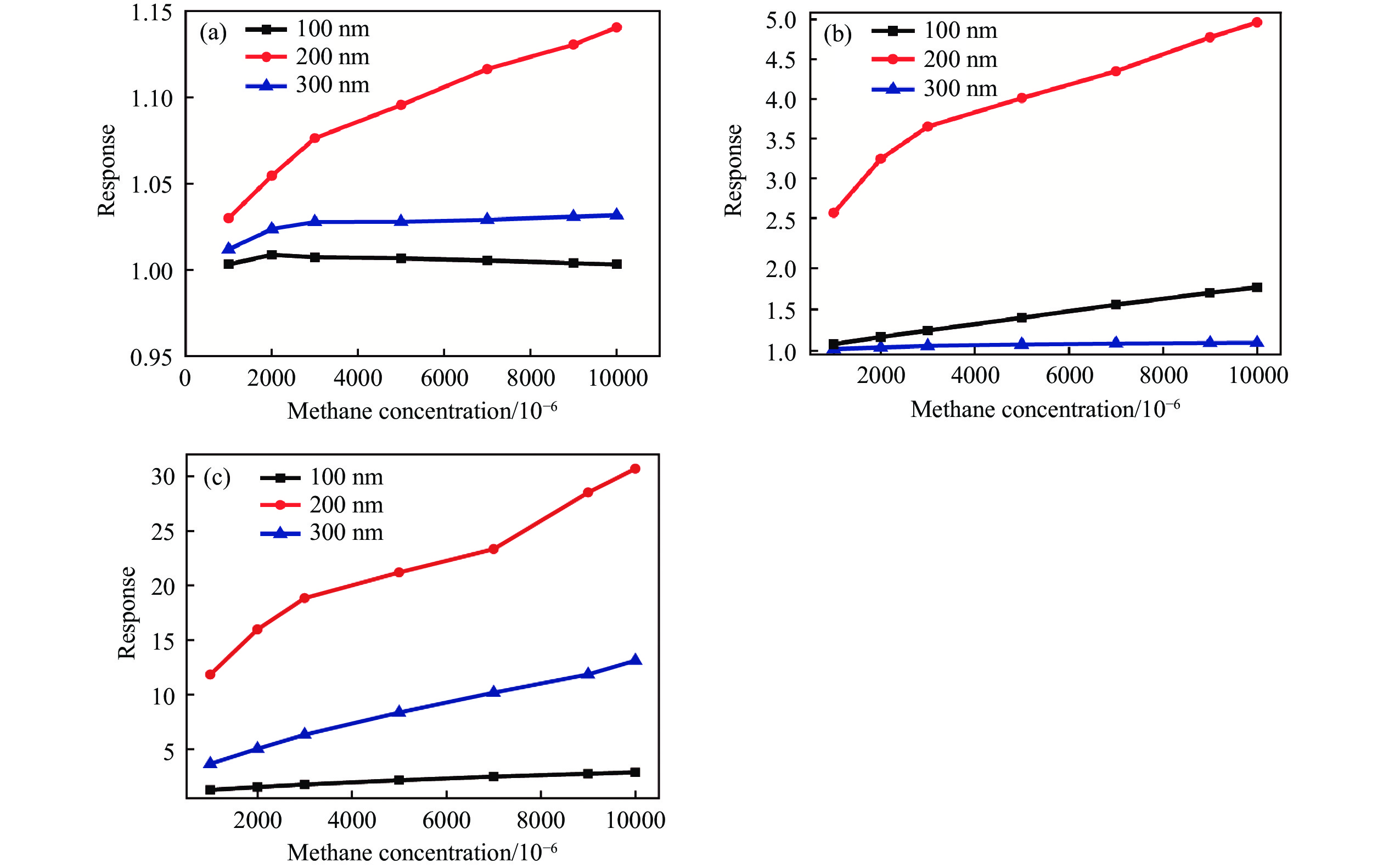
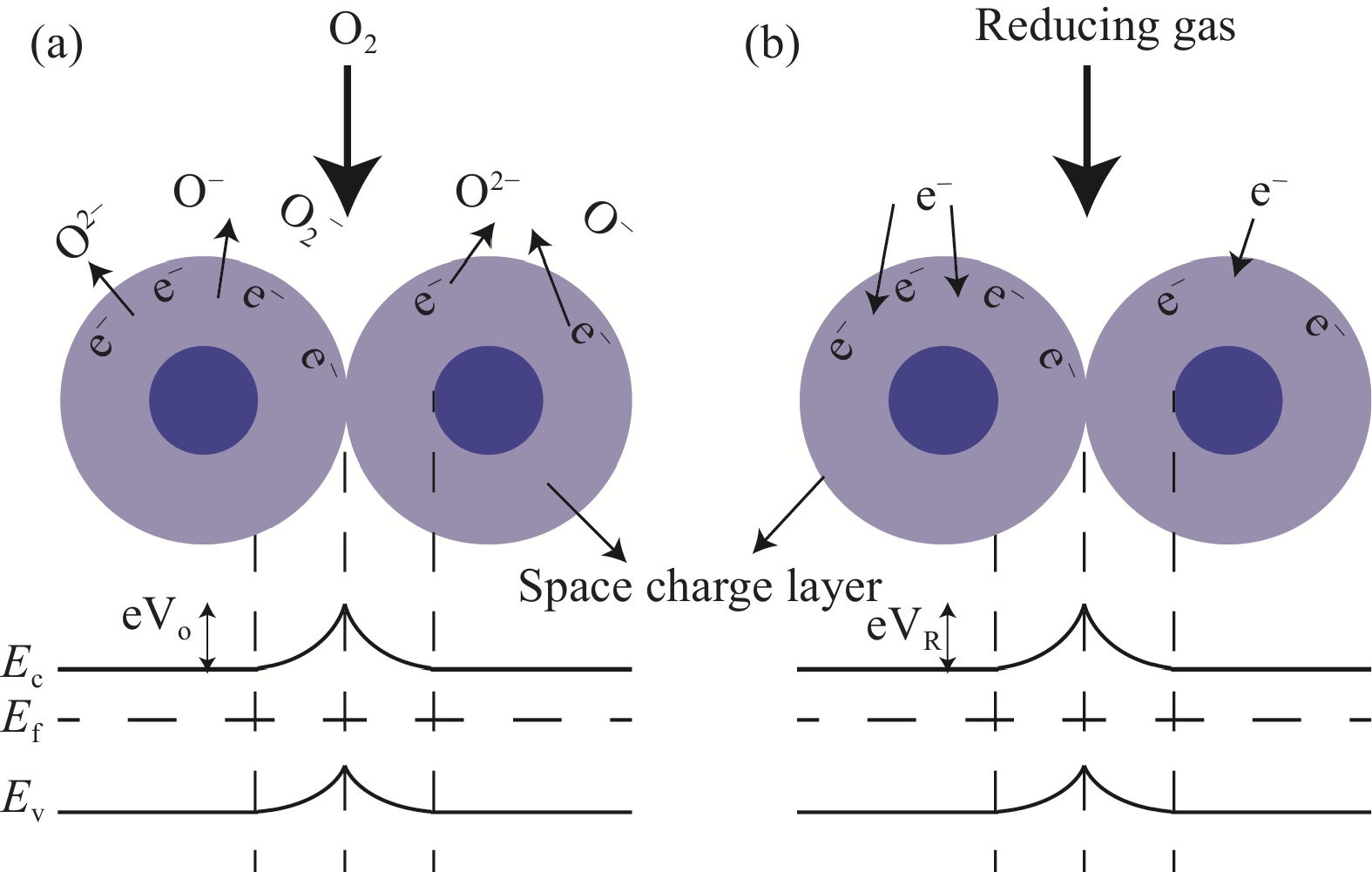
Simulation and performance study of low-power magnetron sputtered ZnO methane sensor
-
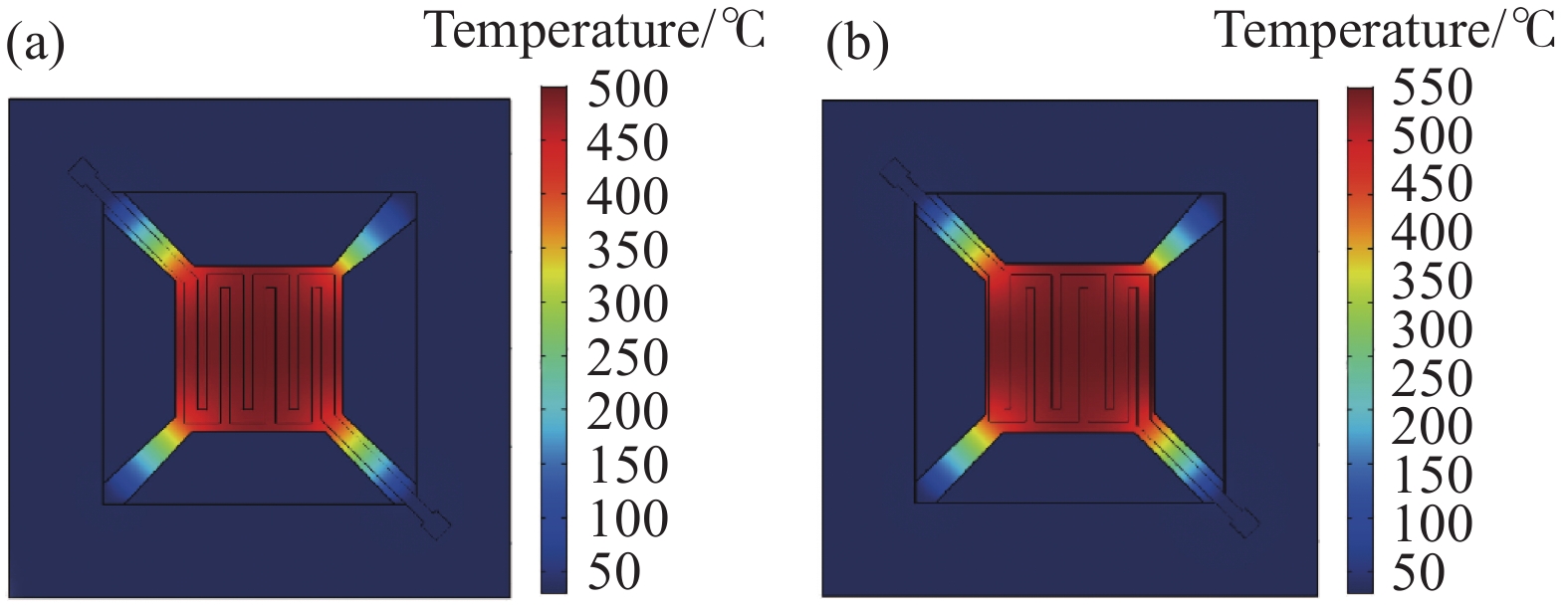
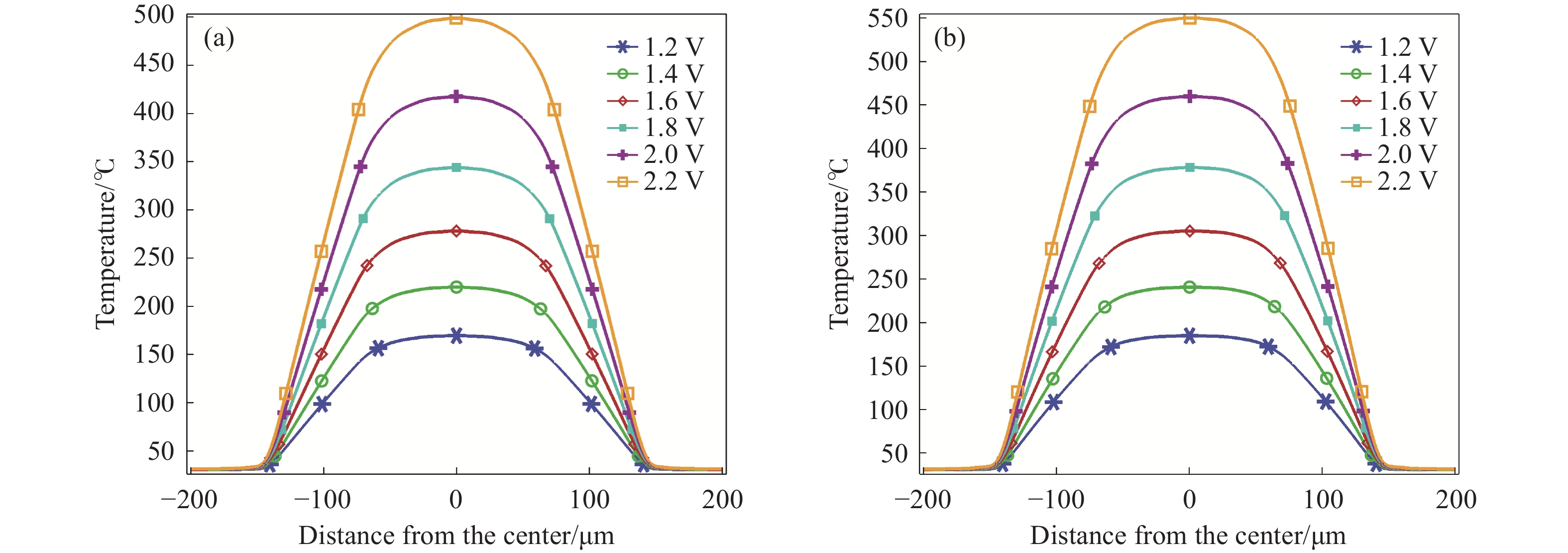
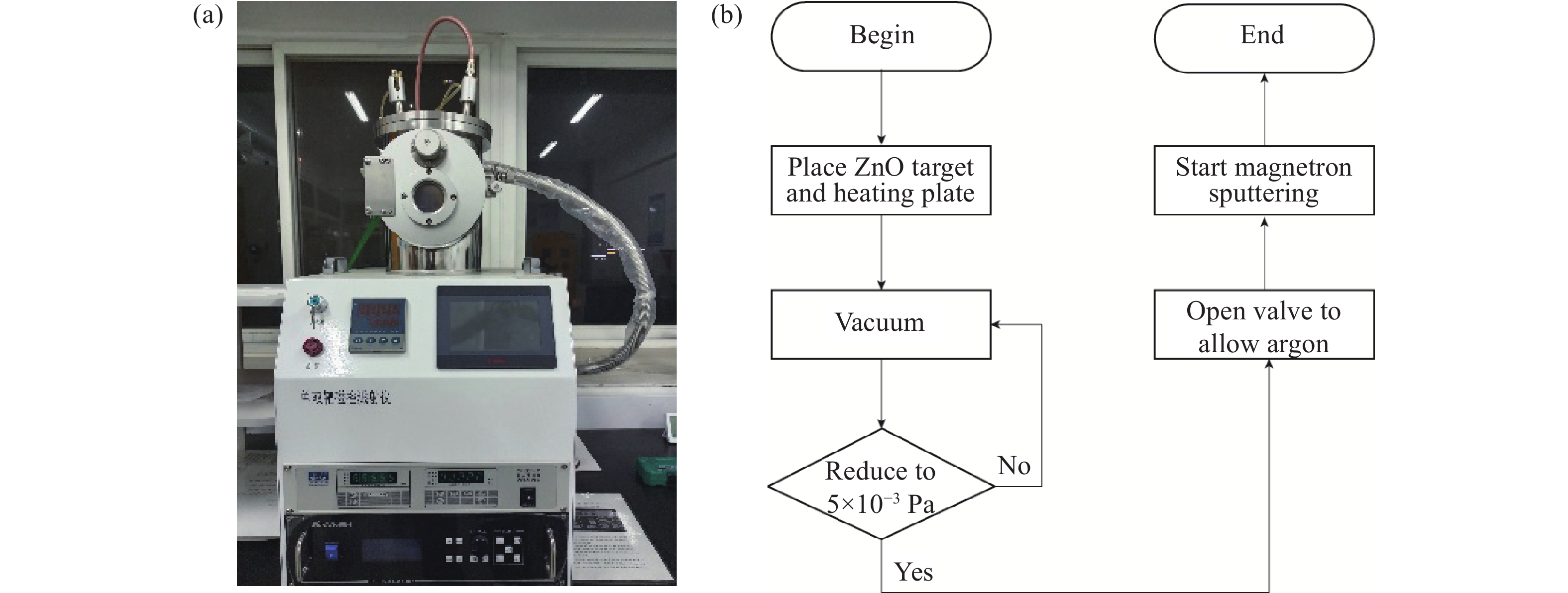
摘要: 隨著微機電系統(MEMS)的發展,運用該技術的半導體傳感器也跟著迅速發展,逐漸走向微型化、集成化和智能化。基于MEMS的微加熱板(MHP)的金屬氧化物甲烷傳感器具有功耗小、響應快等優點,廣泛應用于甲烷檢測。其中,氧化鋅(ZnO)甲烷敏感材料因其靈敏度高、中毒效應小、工作溫度低等優點,廣受關注。但是,該敏感材料制備的傳感器響應性能依然受加熱溫度及熱量分布的強烈影響。使用有限元分析(FEA)軟件COMSOL中的Multiphysics模塊對物理場中的溫度進行仿真分析與比較,揭示了在相同工作條件下加熱電極結構對溫度分布的影響,優選的微加熱板達到300 ℃時需要75 mW左右的功率。在商用微加熱板的叉指電極上采用無遮擋全表面濺射氧化鋅敏感材料構建ZnO薄膜甲烷傳感器,并使用合肥微納公司HIS9010測試了氣體傳感器的響應。采用靜態測量的方法向1 L的氣體腔內注射甲烷氣體,經過測試,與現在不同形貌的ZnO相比,本課題組使用的磁控濺射制備的氧化鋅薄膜氣體傳感器,在(1000~10000)×10?6甲烷濃度區間內響應線性度比較好,對濃度為10000×10?6的甲烷響應值達到了30。與國內外商用甲烷傳感器的甲烷響應性能進行了對比,結果表明本課題組制作傳感器響應更高,更具有應用優勢。Abstract: With the development of the industry of semiconductor integrated circuits, microelectromechanical system (MEMS) products have made rapid progress. The development of MEMS and the combination of sensor technology have yielded compact sensors with increased functions and intelligence levels. MEMS-based microhotplate (MHP)-type metal oxide methane sensors have the advantages of low power consumption and fast response and have been widely used in methane detection applications. In particular, ZnO methane-sensitive materials have attracted significant attention due to their high sensitivity, small poisoning effect, and low operating temperature. Notably, the response performance of sensors prepared from these sensitive materials is still significantly affected by the heating temperature and thermal distribution of the MEMS-based MHP. The purpose of our experiment is to optimize the heat generation of the heating electrodes of MHP, optimize the thermal distribution of MHP, and further reduce the power consumption of MHP sensors. The heating electrodes of MHP are made of platinum materials that have high thermal conductivity and stable performance. In this study, we use the Multiphysics module in the finite element analysis software COMSOL to simulate and analyze the temperature in the physical field for the two structures of serpentine platinum heating electrodes of MHP. By comparison, the structure of the heating electrodes affects the temperature distribution under the same working conditions. The structure with a larger width in the middle of the heating plate electrode and gradually narrowing to both sides generates more heat than that with the same width. When the heating plate reaches 300 ℃, it needs about 75 mW of power. Next, ZnO thin film methane sensors were constructed by sputtering ZnO methane-sensitive materials on the interdigital electrode of a commercial MHP, and the response of the gas sensor was tested using the HIS9010 of Hefei Micro-Nano Company. The static measurement method was used to inject methane gas into a 1-L gas chamber. In order to verify the superior response of our sensor, it has been compared that performance of commercial methane sensors and ZnO methane sensors made by. The response linearity in the interval is relatively good, and the response value for 10000×10?6 methane reaches 30. The response of our fabricated sensor is higher than those of existing domestic and foreign commercial methane sensors, showing significant potential in related applications.
-
Key words:
- methane sensor /
- micro hotplate /
- finite element analysis /
- magnetron sputtering /
- zinc oxide
-
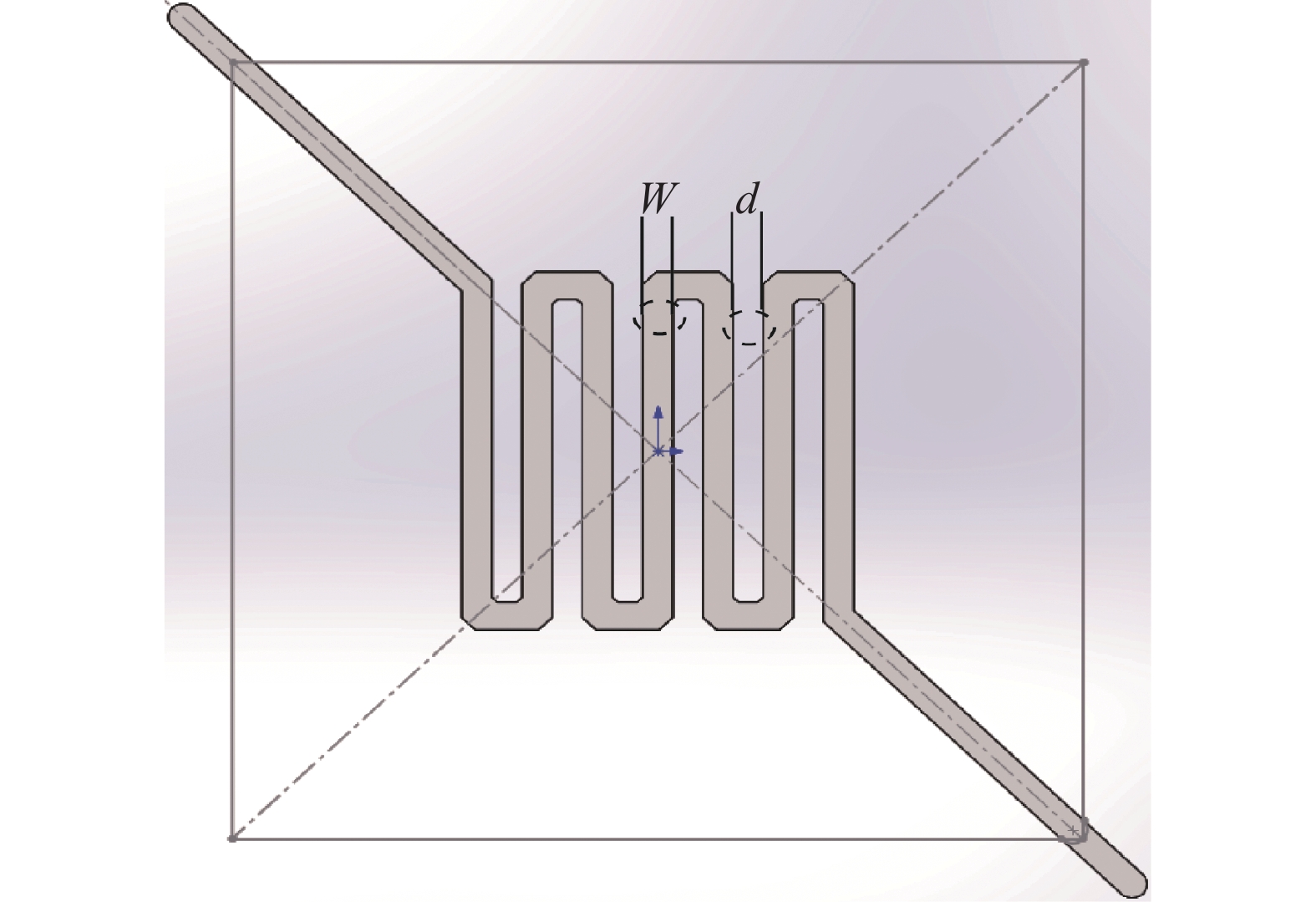
表 1 微加熱板底座及加熱板尺寸
Table 1. MHP base and heating plate dimensions
Structure attribute Specification Silicon substrate Substrate size 1 mm× 1 mm× 0.5 mm Width of platinum heating resistance 1 Width is 12 mm; interval is 10 mm;
thickness is 300 nmWidth of platinum heating resistance 2 Platinum heaters with unequal width. Adjacent spacing is 9 mm; thickness is 300 nm The resistivity of the heating resistance 0.0019 K?1 中文字幕在线观看表 2 甲烷響應對比
Table 2. Comparison of methane responses
Preparation method Methane concentration / 10?6 S References Preparation of ZnO graded structure by hydrothermal method 1000 2.5 [26] ZnO was modified by drop coating with palladium 5000 20 [27] ZnO was modified by g-C3N4 10000 29 [28] Zhengzhou Winsen Electronics Technology Co., Ltd MP-4 1000 10 [9] FIGARO TGS3870 10000 19 [13] Magnetron sputtering ZnO films 1000/5000/10000 12/21/30 This work -
參考文獻
[1] Wang X L, Ji Z G, Xie Y T, et al. Present situation and development trend of gas emission prediction technology in coal face. Sci Technol Eng, 2019, 19(33): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.001王曉蕾, 姬治崗, 謝怡婷, 等. 采煤工作面瓦斯涌出量預測技術現狀及發展趨勢. 科學技術與工程, 2019, 19(33):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.33.001 [2] Zhang T, Zhang Y J, Chang Y R, et al. Methodology of methane emission accounting in petrochemical and chemical industries of China. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci, 2019, 398(1): 012011 doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/398/1/012011 [3] Jiao M Z. Microfabricated Gas Sensors Based on Hydrothermally Grown 1-D ZnO Nanostructures [Dissertation]. Uppsala: Uppsala University, 2017 [4] Ahmad Y H, Mohamed A T, Al-qaradawi S Y. Exploring halloysite nanotubes as catalyst support for methane combustion: influence of support pretreatment. Appl CIay Sci, 2021, 201: 105956 [5] Sha M L, Ma X H, Li N, et al. Dynamical properties of a room temperature ionic liquid: Using molecular dynamics simulations to implement a dynamic ion cage model. J Chem Phys, 2019, 151(15): 154502 doi: 10.1063/1.5126231 [6] Mirzaei A, Leonardi S G, Neri G. Detection of hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by metal oxide nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Ceram Int, 2016, 42(14): 15119 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.145 [7] Zong X H. Research on Gas Sensor Based on Semiconductor Metal Oxide Nanomaterials [Dissertation]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2021宗肖航. 基于半導體金屬氧化物納米材料的氣體傳感器研究[學位論文]. 沈陽: 遼寧大學, 2021 [8] Wang Y, Sun X Y, Cao J L. Enhanced methane sensing performance of Ag modified In2O3 microspheres. J Alloys Compd, 2022, 895: 162557 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162557 [9] Wu Y, Yuan L J, Hua Z Q, et al. Structure optimization of heating plate for MOS gas sensor. Instrum Tech Sens, 2019(10): 12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2019.10.004武一, 苑麗靜, 花中秋, 等. MOS型氣體傳感器加熱板的結構優化. 儀表技術與傳感器, 2019(10):12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2019.10.004 [10] Wang H B. Research progress of low power methane sensor. Ind Mine Autom, 2021, 47(5): 16王海波. 低功耗甲烷傳感器研究進展. 工礦自動化, 2021, 47(5):16 [11] Guo L F, Xu L, Xu Z K, et al. Design and fabrication of micro-nano fusion gas sensor based on two-beam micro-hotplatform. Microsyst Technol, 2017, 23(7): 2699 doi: 10.1007/s00542-016-3091-0 [12] Dong S L, Duan S H, Yang Q, et al. MEMS-based smart gas metering for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J, 2017, 4(5): 1296 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2676678 [13] Xie D C. Study on Low Power Consumption and Array of MEMS MOS Gas Sensors [Dissertation]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2021謝東成. MEMS MOS氣體傳感器的低功耗及陣列化研究[學位論文]. 合肥: 中國科學技術大學, 2021 [14] Peng S F, Xie D C, Wang J, et al. Integration of SnO2 nanoparticles with micro-hot platform for low-power-consumption gas sensors. Sens Mater, 2018, 30(11): 2679 [15] Wang Y, Meng X N, Cao J L. Rapid detection of low concentration CO using Pt-loaded ZnO nanosheets. J Hazard Mater, 2020, 381: 120944 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120944 [16] Yu J, Tang Z A, Yan G Z, et al. An experimental study on micro-gas sensors with strip shape tin oxide thin films. Sens Actuat B Chem, 2009, 139(2): 346 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2009.03.033 [17] Bhattacharyya P, Basu P K, Mondal B, et al. A low power MEMS gas sensor based on nanocrystalline ZnO thin films for sensing methane. Microelectron Reliab, 2008, 48(11-12): 1772 doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2008.07.063 [18] Andio M A, Browning P N, Morris P A, et al. Comparison of gas sensor performance of SnO2 nano-structures on microhotplate platforms. Sens Actuat B Chem, 2012, 165(1): 13 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.12.045 [19] Marasso S L, Tommasi A, Perrone D, et al. A new method to integrate ZnO nano-tetrapods on MEMS micro-hotplates for large scale gas sensor production. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(38): 385503 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/38/385503 [20] Zhang W S, Yuan T W, Wang X H, et al. Coal mine gases sensors with dual selectivity at variable temperatures based on a W18O49 ultra-fine nanowires/Pd@Au bimetallic nanoparticles composite. Sens Actuat B Chem, 2022, 354: 131004 doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.131004 [21] Yuan Z Y, Yang F, Meng F L, et al. Research of low-power MEMS-based micro hotplates gas sensor: A review. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21(17): 18368 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3088440 [22] Arun K, Lekshmi M S, Suja K J. Design and simulation of ZnO based acetone gas sensor using COMSOL Multiphysics // Proceedings of 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN). Noida, 2020: 659 [23] Wu PJ, Liu WQ, Yang YL, et al. Room temperature gas sensing properties of ZnO/p-Si porous nano-film heterojunction prepared by magnetron sputtering. Electron Compon Mater, 2021, 40(12): 1184吳鵬舉, 劉文強, 楊瑩麗, 等. 磁控濺射制備ZnO/p-Si多孔納米薄膜異質結及其室溫氣敏特性. 電子元件與材料, 2021, 40(12):1184 [24] He Y, Sun B Y, Jiang L, et al. Effect of Ag doping on SnO2 sensing for detecting H2S: A first-principles study. Vacuum, 2021, 194: 110587 doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110587 [25] Jiao M Z, Chen X Y, Hu K X, et al. Recent developments of nanomaterials-based conductive type methane sensors. Rare Met, 2021, 40(6): 1515 doi: 10.1007/s12598-020-01679-9 [26] Yang Y Q, Wang X D, Yi G Y, et al. Hydrothermally synthesized ZnO hierarchical structure for lower concentration methane sensing. Mater Lett, 2019, 254: 242 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.07.081 [27] Wang Y, Meng X N, Yao, M X, et al. Enhanced CH4 sensing properties of Pd modified ZnO nanosheets. Ceram Int, 2019, 45(10): 13150 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.250 [28] Li X J, Li Y W, Sun G, et al. Synthesis of a flower-like g-C3N4/ZnO hierarchical structure with improved CH4 sensing properties. Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(5): 724 doi: 10.3390/nano9050724 -




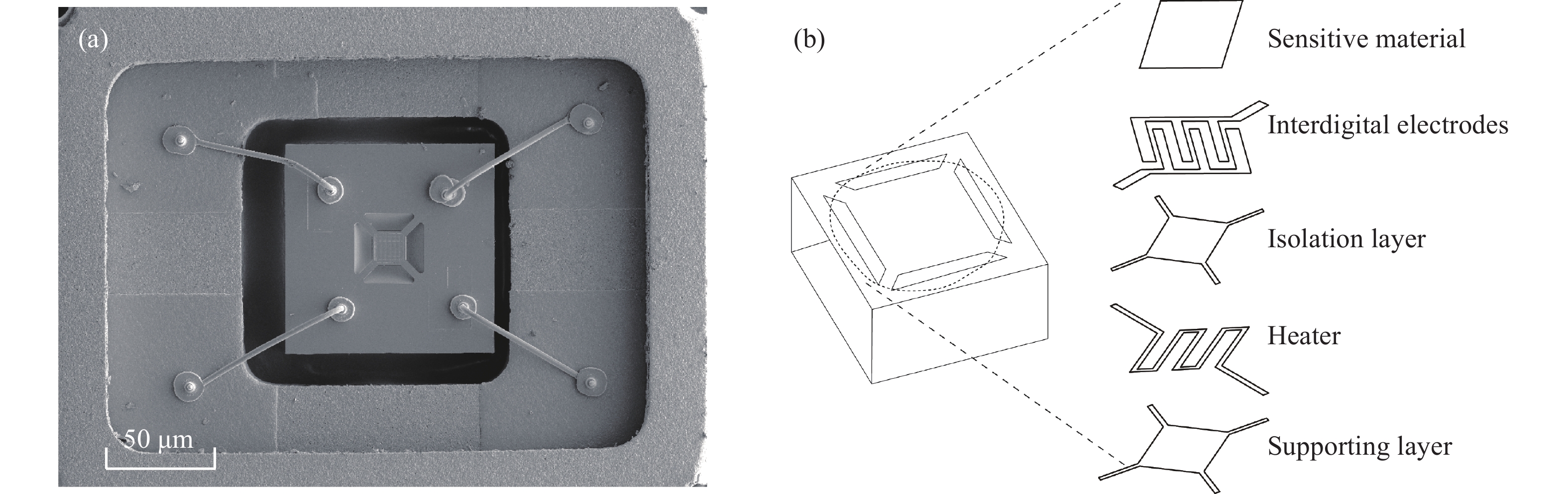
 下載:
下載: